- © 2018 - 2022 ProVen Probiotics. Cultech
- Contact Us
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Probiotics and Endometriosis: A New Approach to Treatment
Understanding Endometriosis and its Challenges
Endometriosis is a chronic condition that affects 1 in 10 women worldwide. This number is much higher among those struggling with infertility. It can go as high as 50%.
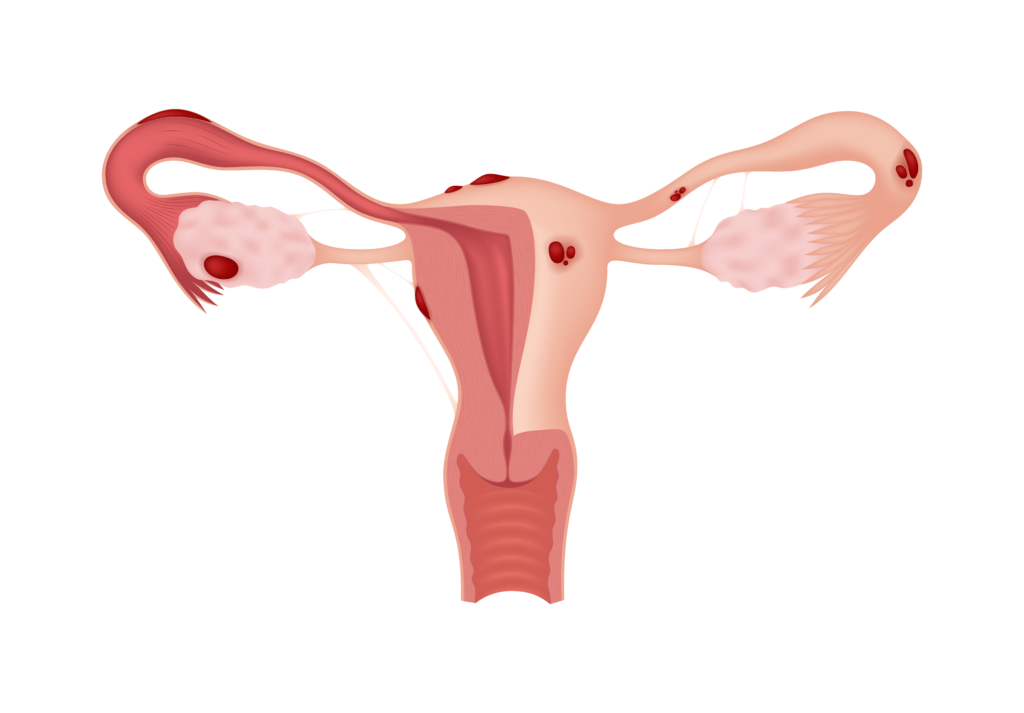
Regular severe pelvic pain is one of the main indicators of endometriosis even before a diagnosis. In most cases, women with this pelvic pain are diagnosed with 9 out of every 10 adults or 4-5 out of every 10 among teenagers. While the causes may not yet be fully understood, we know a few things about the condition.
It is thought to be caused by genetics, environment, hormonal factors, or a combination. Other causal hypothesises include retrograde menstruation, cellular metaplasia, and stem cells (WHO).
Diagnosis is challenging because most symptoms are commonly associated with other illnesses. Physicians would likely use a process of elimination, starting with menstruation and other causes of similar pain, before recommending tests required to confirm endometriosis.
So what is endometriosis? It is when there is the growth of uterus lining-like tissue outside the uterus. The most commonly affected areas include ovaries, fallopian tubes, or the bladder and the bowel. This growth starts with pain, followed by scarring and eventually infertility.
There are two major challenges with endometriosis, diagnosis and the absence of a cure. Without a cure, all the focus is on managing the symptoms.
The Link Between Gut Health and Endometriosis
The link between gut health and endometriosis is an area of growing interest, although the exact mechanisms and causality are not fully understood. Several factors suggest a possible connection between gut health and endometriosis, such as altered gut microbiota composition, which can lead to changes in gut permeability, inflammation, immune responses and hormone metabolism including oestrogen levels. These factors could potentially affect the development or progression of endometriosis.
What are Probiotics and How Can They Help?
Probiotics are live microorganisms such as bacteria and yeasts. They are incorporated into our diets, in the form of yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut and kefir or in the form of dietary supplements. Their potential role in managing endometriosis is still being explored with some studies suggesting that imbalance in gut microorganisms (dysbiosis) may contribute to inflammatory conditions. Probiotics are known to help maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota and improve overall gut health, which could potentially have a positive impact on endometriosis symptoms.
Probiotics and Hormonal Balance: A Promising Connection
There is evidence indicating the positive effects of probiotics on hormonal balance. A 2011 study looked at the effect of probiotics and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and found a positive impact among perimenopausal women. Probiotics were found to impact hormonal homeostasis. This represents the potential for non-evasive treatment for hormonal imbalance, which is promising.
The recent review looking at Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), found that probiotics positively impacted the hormonal levels and reduced inflammation.
Studies on Probiotics and Endometriosis: What Do They Say?
Probiotics containing the Lactobacillus strains have been identified as helpful to the female reproductive tract’s health, which is affected by the illness. Furthermore, low Lactobacillus endometrial microbiota has been linked to fertility issues. The evidence regarding the specific benefits of probiotics for endometriosis is limited and inconclusive. More research is needed to establish the effectiveness of probiotics in the management of endometriosis.
One study focused on the interaction between steroid hormones and the epigenome, which refers to the modifications of DNA and associated proteins that can control gene expression without altering the genetic code itself. The results of the study indicated that the response to oestrogen, progesterone, and their combination varied between healthy women and those with endometriosis. These findings have important implications for understanding the underlying mechanisms of the condition and its impact on fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
Probiotics and Natural Approaches to Managing Endometriosis Symptoms
Before incorporating probiotics into your diet to help with endometriosis, it is important to consult your doctor. The health professionals can provide personalised advice based on your specific condition and medical history and may also recommend potential dietary and lifestyle modifications and other treatment options, such as hormonal therapies or pain management strategies, such as acupuncture, Ayurveda, physiotherapy or biofeedback.

 Available from the 8th March to the 19th March on our three most popular women’s probiotics.
Available from the 8th March to the 19th March on our three most popular women’s probiotics.  Discount added automatically at checkout for you.
Discount added automatically at checkout for you. 