ProChild-2 Study
Probiotics with vitamin C for the prevention of upper respiratory tract symptoms in children aged 3-10 years: randomized controlled trial
Aim
Method
Results
URTI symptoms
• 16% significant reduction in the incidence of coughing in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (Fig 1, *P<0.05).
• 20% significant reduction in the incidence of sore throats in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (Fig 1, *P<0.05).
• Only 5.8% children in Group 2 had all five URTI symptoms on one day compared to 18.8% children in Group 1 (P<0.05). URTI symptoms included cough, sore throat, sneezing, runny/blocked nose.
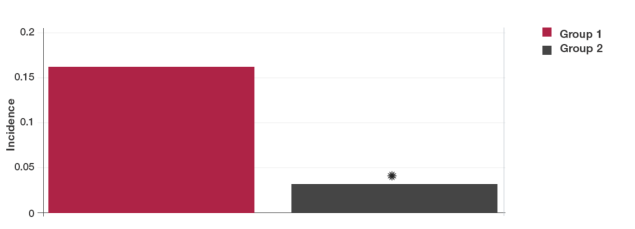
• 79% significant reduction in the incidence of episodes with all five URTI symptoms on one day (Fig 2, *P<0.0001)
Fig 1 Incidence of URTI symptoms
Fig 2 Incidence of all five URTI symptoms on one day
Paediatric physician’s visit and antibiotic usage
- Over the 6-month study period, the number of visits to the G.P for any reason was significantly reduced by 19% (Fig 4, *P<0.05)
- Significant reduction in antibiotic use by 27% in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (Fig 4, *P<0.05).
Fig 4 Incidence of GP visits and antibiotic usage
Conclusion
Lab4 probiotics in combination with low dose of vitamin C reduce the incidence of coughing, sore throats together with absence from school and antibiotic use.
To our knowledge, this is the first time two probiotic studies (ProChild and ProChild-2) with the same intervention for same duration showed the beneficial effect in the management of URTIs in children attending school.

 Available from the 8th March to the 19th March on our three most popular women’s probiotics.
Available from the 8th March to the 19th March on our three most popular women’s probiotics.  Discount added automatically at checkout for you.
Discount added automatically at checkout for you. 



